Engage
Where are lithium-ion batteries in our community?
Click on the hotspots below to discover devices that use lithium-ion batteries. Think about similarities and differences you notice between these devices. And be on the lookout for things you use and see in your own life…
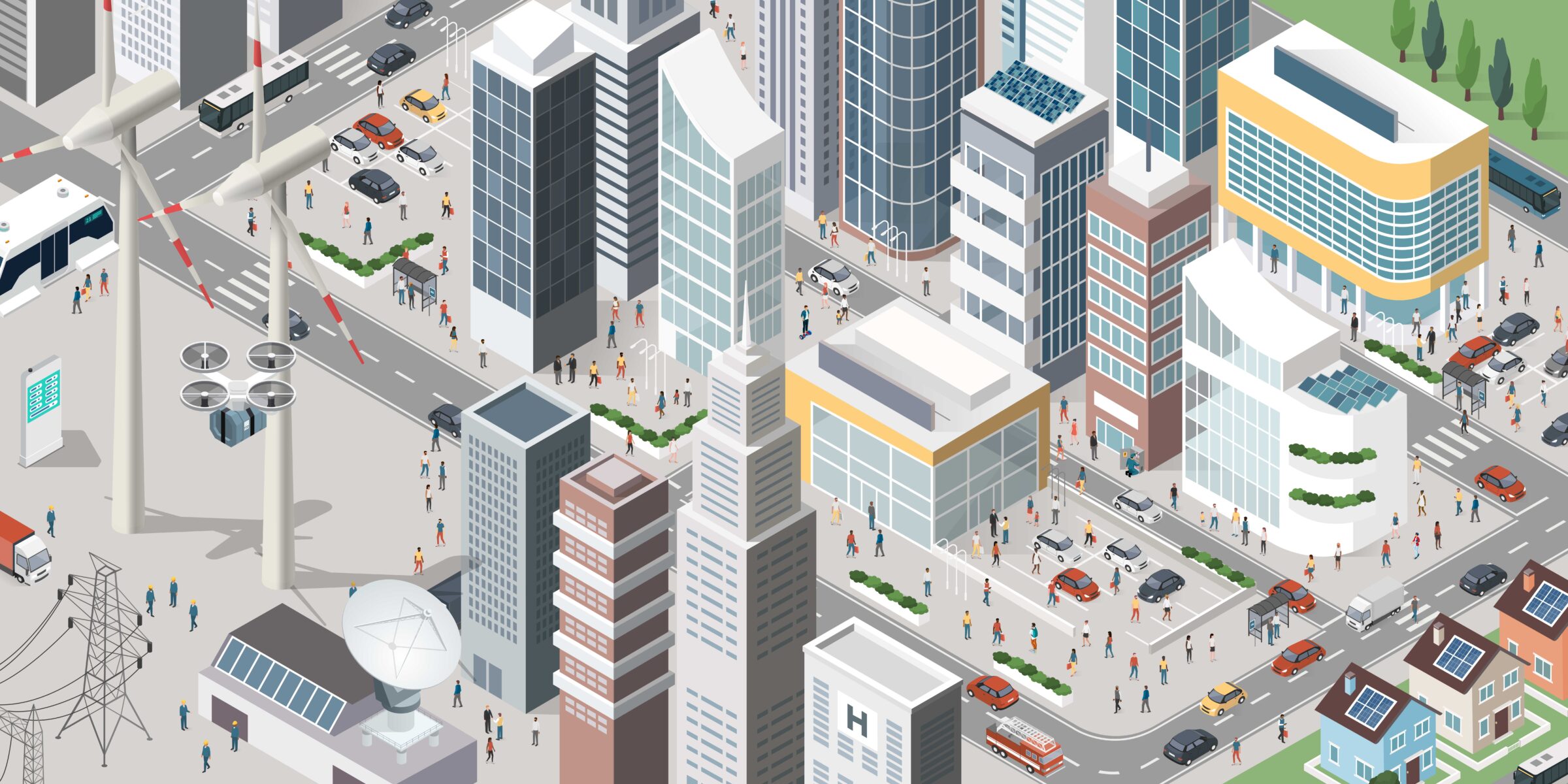

Subways and Light Rail
Trains are a piece of public transit systems that bring us from place to place. Lithium-ion batteries can be a part of this system. For example, in some cities, trains use lithium-ion batteries in the brake system to store kinetic energy and use it later.

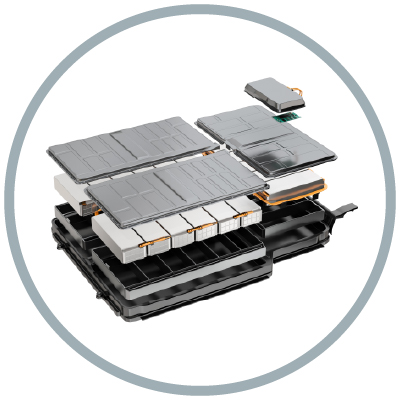
Electric vehicles
Whispery silent vehicles are becoming a preferred choice of transportation – but did you know the batteries that power them aren’t that different from the ones in your phone? Lithium-ion batteries power electric cars, bikes, and scooters.

Virtual reality
Virtual reality (VR) technology creates immersive, interactive environments. Lithium-ion batteries power VR headsets and controllers.

Mobile phones
Mobile phones help us stay connected to one another no matter where in the world we are. They are powered by lithium-ion batteries.

Stationary energy storage
Lithium-ion batteries can store energy for future use as stationary energy storage so it can be used when it is needed.

Drones:
Drones are flying vehicles that are unpiloted or piloted with a remote control. Drones are useful for tasks like search and rescue, aerial photography, and delivering packages. Lithium-ion batteries power these devices.

Headphones
Lithium-ion technology grants batteries the flexibility to be small and rechargeable. These qualities allow them to power devices like wireless earbuds and headphones.

Hoverboards
Lithium-ion batteries power novel forms of transportation such as self-balancing scooters.

Power tools
Cordless power tools facilitate construction in places that lack electrical outlets. These tools are often powered by lithium-ion batteries.

Smart watches
Smart watches and other wearables do more than just tell the time. These rechargeable, small devices can monitor heart rate, connect to the internet, and use GPS. They are powered by lithium-ion batteries.

Tablets
Tablets have the capabilities of a smartphone with a larger screen. These powerful, portable devices are fueled by lithium-ion batteries.

Portable chargers
Lithium-ion batteries can store energy for future use in portable power banks so that you can charge your devices on the go.

Satellites
Satellites orbit the planet. They transmit telecommunications like TV, internet, and phone. They inform GPS and meteorology systems. Satellites are powered by solar power, which is stored in lithium-ion batteries for use when the satellites are in the Earth’s shadow.

Medical devices
Medical devices like blood glucose meters can support and monitor health conditions over extended periods of time. These devices are sometimes powered by lithium-ion batteries.

Solar panels
Renewable energy sources like solar vary in how much energy they can provide at a given time. Lithium-ion batteries store this energy so that it can be used consistently.